See previous preparatives in:
How to install App-V deployment infrastucture: Chapter 1
At this point we have two computers, one installed with Windows Hyper-V server 2011, ant the other installed with Windows 7 Enterprise with Service Pack 1, and the RSAT. (Take care about this SP1, because we are going to need it a few times).
Using the RSAT, we must access to the Hyper-V and create and install four virtual machines with the following requirements, Operative Systems and Aditional Software installed on each one: (The Domain Controller is not recommend to be installed as a virtual machine, but for this trial we are going to do it virtualized).
Domain Controller: ADDS Server
A Windows 2008 R2 with the Active Domain Role installed. Also we need to create the following objects into the Active Domain.
- An Organizational Unit named AppVObjects to store all the following objects.
- A group named AppV Administrators. Put the Domain Administrator into this group.
- A group named AppV Computers.
- A group named AppV Users.
- A user named Usuario1. Put this user inside the AppV Users.
- A user named Usuario2.
App-V Server
A Windows 2008 R2 with the Service Pack 1 installed and joined to the domain in ADDS Server.
Install the following software packages:
- .Net Framework 4
- Visual C++ 2010 SP1 Redistribuitable 64bits.
- Microsoft Silverlight.
- Powershell 3.0
Install the Application Server role with the .Net Framework 3.5.1 feature.
Install the IIS 7.5 for Windows 2008 R2 with the following features:
- Common HTTP features (Static Content / Default Document)
- Application Development (ASP.Net / .Net Extensibility / ISAPI Extensions / ISAPI Filters )
- Security ( Windows Authentication / Request Filtering )
- Management tools ( IIS Management Console )
Register ASP.Net with the .Net Framework 4.0 on IIS running the following at the command line:
c:\windows\Microsoft.Net\Framework\V4.030319 aspnet_regiis.exe -ir
c:\windows\Microsoft.Net\Framework64\V4.030319 aspnet_regiis.exe -ir
Install SQL Server 2008 R2. Note that you can´t use the express edition. You could use the standar, evaluation, or any other one. Also is important that you install the SQL server logged as the domain administrator.
During the installation of SQL Server you must consider the following points:
- On the Setup Role window select SQL Server Feature Installation.
- On the Feature Selection select Database Engine Services.
- On the Server Configuration click over Use the same account for all SQL Server services, and in the account name enter NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM, click Ok, and change all Startup Types to Automatic.
- On the Database Engine Configuration click Add Current User to add de Administrator domain, if you are not logged as him then add it mannually.
Once we have installed SQL Server now it´s time to install the Appv Management and Publishing Server, so we must run appv_server.exe to do it. It is recommended to install both servers in separate machines, but for this time we are going to install together in the same machine.
These are the steps we must perform during the installation process:
- On the feature Selection, select Management Server, Management Server DB and Publishing Server.
- On the Management Server Configuration windows and on the Publishing server configuration use the following configuration:
If you obtain the followuing error message after clicking over Next in the Management Server Configuration is because you are not logged with the Domain Administrator.
Take notice that we have used the Management Server as the Publishing server, an also that we have used
http://localhost:5353. This is becacuse there is a bug in the App-V 5.0 Beta when the Management and Publishing servers are hosted in the same machine that causes an error 500 and trying to access the Publishing site.
Now we must create a folder at C:\ in the server named Content, and we must gave full permission to the AppV Administrators, and the Computer. In this folder we must put the sequenced applications. You could see in another post how to sequence an applicattion.
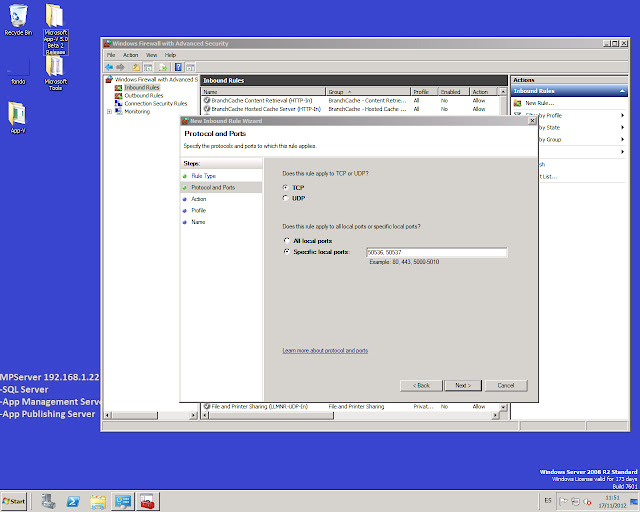
It´s time to create a new rule for the windows firewall to avoid block access to the ports defined in the AppV Server for management and publishing. So we go to Control Panel, Windows Firewall and Advanced Settings and create a new rule enabling the ports 50536 and 50537.
The final part of the installation is to publish an application into the AppV Center. To do this we must go to the Management console with an Internet Explorer typing http://localhost:50536/console.html. First we must go to Server and add the actual server. Later we must type the direction to the sequenced application and add it to the publishing center. Its important to use an UNC or HTTP path type to the location of the application to publish.
Once we have installed AppV Server, we have the ports opened for the firewall, and we have the application sequenced placed at the content folder, it´s time to try if all is ok. First we could try the Management server by opening an Internet Explorer and typing http://localhost:50536 or
http://localhost:50536/Help. We must obtain the following responses if the Management Site is ok.
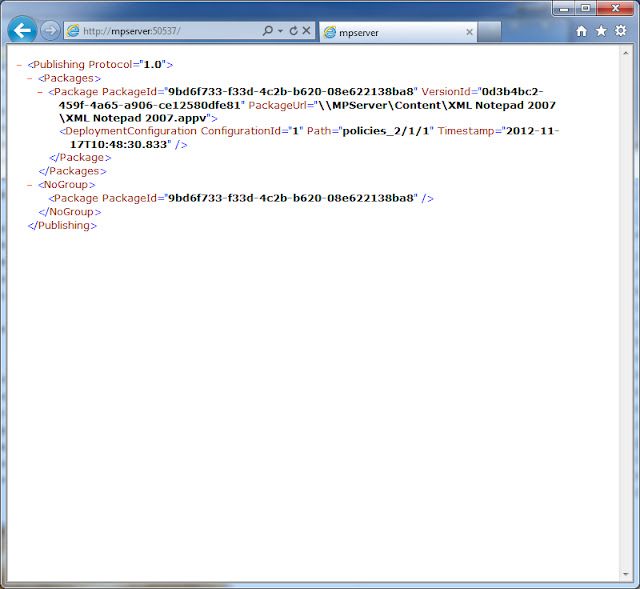
To test the publishing server we must type http://localhost:50537 from a I.e. at the server, or http//appvcenter:50537 from a computer client. In that case we would obtain a window showing the applications sequenced into the App Server. (The picture above shows the Publishing server accesed from a client computer).
Here you can see the IIS config window after the installation process:
Also you can see the registry typing regedit at the command line to see the configuration for the Management and Publishing server:
App-V Client
A Windows 7 with the Service Pack 1 installed and joined to the domain in ADDS Server and with at least 40GB of Hard Disk.
Install the following software packages:
- .Net Framework 4
- Powershell 3.0
Install as an administrator the Appv_client.
Using Powershell run the following commands:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
Import-Module AppvClient
Add-AppvPublishingServer -Name App-V PubS -URL http://appcenter:50537
Set-AppvPublishingServer -ServerId 1 -GlobalRefreshEnabled 1 -GlobalRefreshOnLogon 1
If you want to make any change to this parameters you need to remove the Publishing server using the powershell and the command, and adding again with the same commands used previously.
Remove-AppvPublishingServer -ServerID 1
Other way to do it is editin the registry with regedit.
And that´s all, now you can restart the Client machine and login with the user Usuario1 and the virtual apllication must appear in the desktop and in the programas menu. On the other hand if you used the Usuario2 to log into the client, the virtual application will not apper because Usuario2 is not a member of the AppV Users, wich is the only group allowed to the XML Notepad virtual application.